Lesson 1
Preface
Please log in to save materials. Log in
- Subject:
- Social Science, Psychology
- Material Type:
- Full Course
- Level:
- Community College / Lower Division, College / Upper Division
- Provider:
- Rice University
- Provider Set:
- OpenStax College
- Tags:
-
- 1
- ADHD
- Abnormal Motor Behavior
- Abnormal Psychology
- Abraham Maslow
- Absentmindedness
- Absolute Threshold
- Abu Ghraib
- Accommodation
- Acoustic Encoding
- Acquisition
- Action Potential
- Actor-observer Bias
- Add
- Addiction
- Addiction Treatment
- Adler
- Adolescence
- Adrenal Gland
- Adrenarche
- Afterimage
- Ageism
- Aggression
- Agonist
- Agoraphobia
- Alarm Reaction
- Alfred Adler
- Algorithm
- All-or-none
- Allele
- Alpha Wave
- Altruism
- American Psychiatric Association
- American Psychological Association
- Americans With Disabilities Act
- Amnesia
- Amplitude
- Amygdala
- Anabolic Steroid
- Anal Stage
- Analytical Intelligence
- Analytical Psychology
- Anchoring Bias
- Anger
- Animal Research
- Anorexia Nervosa
- Antagonist
- Anterograde Amnesia
- Antisocial
- Antisocial Personality Disorder
- Anxiety Disorder
- Appraisal
- Archetype
- Archival Research
- Arousal
- Arousal Theory
- Artificial Concept
- Asch Effect
- Assimilation
- Associative Learning
- Asthma
- Asylum
- Atkinson-Shiffrin Model
- Attachments
- Attention
- Attention Deficit Disorder
- Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder
- Attitude
- Attraction
- Attribution
- Attrition
- Atypical
- Auditory Cortex
- Auditory System
- Authoritarian Parenting Style
- Authoritative Parenting Style
- Autism Spectrum Disorder
- Automatic Processing
- Autonomic Nervous System
- Availability Heuristic
- Aversive Conditioning
- Avoidance Personality Disorder
- Avoidant Attachment
- Axon
- B. F. Skinner
- BFOQ
- BMI
- Bad Stress
- Bandura
- Bariatric Surgery
- Basilar Membrane
- Basolateral Complex
- Behavior Modification
- Behavior Therapy
- Behavioral Genetics
- Behaviorism
- Bias
- Big Five Personality Traits
- Binaural Cue
- Binge Eating Disorder
- Binocular Cue
- Binocular Disparity
- Biofeedback
- Biological Psychology
- Biological Rhythm
- Biomedical Therapy
- Biopsychology
- Biopsychosocial Model
- Bipolar Disorder
- Bipolar and Related Disorders
- Bisexual
- Blind Spot
- Blocking
- Body Dysmorphic Disorder
- Body Language
- Body Mass Index
- Bona Fide Occupational Qualification
- Borderline Personality Disorder
- Bottom-up Processing
- Brain
- Brain Imaging
- Brain Scan
- BranchED Foundations
- BranchED SEL
- BranchEd
- Broca's Area
- Bulimia Nervosa
- Bullying
- Bystander Effect
- C-TCB
- CPAP
- CT Scan
- Cannon-Bard
- Cannon-Bard Theory of Emotion
- Cardiovascular Disorder
- Careers in Psychology
- Carl Jung
- Carl Rogers
- Case Studies
- Case-study
- Cataplexy
- Catatonic Behavior
- Causality
- Cause and Effect
- Cause-and-effect Relationship
- Central Nervous System
- Central Nucleus
- Central Route Persuasion
- Central Sleep Apnea
- Cerebellum
- Checklist
- Chemical Senses
- Chromosome
- Circadian Rhythm
- Classical Conditioning
- Client-centered Therapy
- Clinical Psychology
- Clinical Study
- Closure
- Cochlea
- Cochlear Implant
- Codeine
- Cognition
- Cognitive Behavior Therapy
- Cognitive Development
- Cognitive Dissonance
- Cognitive Empathy
- Cognitive Map
- Cognitive Psychology
- Cognitive Script
- Cognitive Therapy
- Cognitive-behavioral Therapy
- Cognitive-mediational Theory
- Collective Unconscious
- Collectivist Culture
- Color Vision
- Commission
- Comorbid Disorder
- Comorbidity
- Companionate Love
- Compliance
- Components of Emotion
- Compulsion
- Computerized Tomography
- Concept
- Conception
- Concrete Operational Stage
- Conditioned Response
- Conditioned Stimulus
- Conditioning
- Conductive Hearing Loss
- Cone
- Confederate
- Confidentiality
- Confirmation Bias
- Conformity
- Confounding Variable
- Congenital Analgesia
- Congenital Deafness
- Congenital Insensitivity to Pain
- Congruence
- Conscious
- Consciousness
- Conservation
- Constrict
- Construction
- Consummate Love
- Contemporary Psychology
- Contemporized-Themes Concerning Blacks Test
- Continuity
- Continuous Development
- Continuous Positive Airway Pressure
- Continuous Reinforcement
- Control Group
- Convergent Thinking
- Coping
- Coping With Stress
- Cornea
- Corpus Callosum
- Correlation
- Correlation Coefficient
- Correlational Research
- Cortisol
- Counseling Psychology
- Counterconditioning
- Couples Therapy
- Creative Intelligence
- Creativity
- Crest
- Critical (sensitive) Period
- Cross-sectional Research
- Crystallized Intelligence
- Cultural Competence
- Cultural Display Rule
- Cultural Intelligence
- Culture
- Cyberbullying
- DARE
- DNA
- DNR
- DSM
- DSM-5
- Daily Hassles
- Darwin
- De Novo Mutations
- Deaf Culture
- Deafness
- Death
- Debriefing
- Deception
- Decibel
- Declarative Memory
- Deductive Reasoning
- Defense Mechanism
- Deinstitutionalization
- Delta Wave
- Delusion
- Dendrite
- Deoxyribonucleic Acid
- Dependent Personality Disorder
- Dependent Variable
- Depersonalization Disorder
- Depressant
- Depression
- Depressive Disorder
- Depth Perception
- Derealization Disorder
- Developmental Milestones
- Developmental Psychology
- Diagnosis
- Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders
- Diathesis Stress Model
- Difference Threshold
- Dilated
- Discontinuous Development
- Discrimination
- Disorganized Attachment
- Disorganized Motor Behavior
- Disorganized Thinking
- Displacement
- Dispositional
- Dissertation
- Dissociative Amnesia
- Dissociative Disorder
- Dissociative Fugue
- Dissociative Identity Disorder
- Distorted Body Image
- Distress
- Divergent Thinking
- Do Not Resuscitate
- Dominant Allele
- Dopamine Hypothesis
- Dorothea Dix
- Double-blind Study
- Downsizing
- Dream Analysis
- Drive Theory
- Drug Abuse
- Drug Abuse Resistance Education
- Drug Addiction
- Drug Use
- Dying
- Dysgraphia
- Dyslexia
- EEG
- Eating
- Eating Disorder
- Effortful Processing
- Ego
- Egocentrism
- Elaboration Likelihood Model
- Elaborative Rehearsal
- Electroconvulsive Therapy (ECT)
- Electroencephalography
- Electromagnetic Spectrum
- Embryo
- Emerging Adulthood
- Emotion
- Emotion-focused Coping
- Emotional Expression
- Emotional Intelligence
- Empathy
- Empirical
- Empiricism
- Employment
- Encoding
- Endocrine System
- Engram
- Epigenetics
- Episodic Memory
- Equipotentiality Hypothesis
- Eric Erikson
- Erickson
- Erik Erikson
- Ethics
- Etiology
- Euphoric High
- Eustress
- Event Schema
- Evidence Based Practice
- Evolution
- Evolutionary Psychology
- Excitement
- Experimental Group
- Experimenter Bias
- Explicit Memory
- Exposure Therapy
- Extinction
- Extrinsic Motivation
- Eyewitness
- FMRI
- FREQUENCY
- Facial Expression
- Facial Feedback Hypothesis
- Fact
- False Correlation
- False Memory Syndrome
- Falsifiable
- Family Therapy
- Fear
- Feminist Psychology
- Fetal Development
- Fight or Flight
- Figure-ground Relationship
- Fine Motor Skills
- Five Factor Model
- Fixed Interval Schedule
- Fixed Ratio Schedule
- Flashback
- Flashbulb Memory
- Flight of Ideas
- Flow
- Fluid Intelligence
- Flynn Effect
- Foot-in-the-door Technique
- Forebrain
- Forensic Psychology
- Forgetting
- Formal Operational Stage
- Fovea
- Fraternal Twin
- Frederick Taylor
- Free Association
- Frontal Lobe
- Functional Fixedness
- Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging
- Functionalism
- Fundamental Attribution Error
- GLIA
- Gender Dysphoria
- Gender Identity
- Gene
- General Adaptation Syndrome
- Generalize
- Generalized Anxiety Disorder
- Generational Difference
- Genetic Environmental Correlation
- Genetics
- Genital Stage
- Genotype
- Gestalt
- Gestalt Psychology
- Glial Cell
- Gonad
- Gonadarche
- Good Continuation
- Good Stress
- Grammar
- Grandiose Delusion
- Gross Motor Skills
- Group Polarization
- Group Therapy
- Groupthink
- Gustation
- Gyri
- HPA Axis
- Habit
- Hair Cell
- Hallucination
- Hallucinogen
- Hans Eysenck
- Hans Selye
- Happiness
- Harmful Dysfunction
- Hassles
- Hawthorne Effect
- Health Psychology
- Hearing
- Heart Attack
- Heart Disease
- Hemisphere
- Heritability
- Hertz
- Heterosexual
- Heterozygous
- Heuristic
- Hierarchy of Needs
- Higher-order Conditioning
- Hindbrain
- Hindsight Bias
- Hippocampus
- History of Psychology
- Histrionic Personality Disorder
- Hoarding Disorder
- Homelessness
- Homeostasis
- Homophily
- Homophobia
- Homosexual
- Homozygous
- Hopelessness Theory
- Hormone
- Hospice
- Hostile Aggression
- Hostility
- How to begin
- Human Factors Psychology
- Human Research
- Humanism
- Humanistic Therapy
- Hunger
- Hyperactivity Autism Spectrum Disorder
- Hypertension
- Hyperthymesia
- Hypnogram
- Hypnosis
- Hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal Axis
- Hypothalamus
- Hypothesis
- I/O Psychology
- IACUC
- ICD
- ID
- IRB
- Ideal Self
- Identical Twin
- Illusory Correlation
- Imitation
- Immune System
- Immunosuppression
- Immutable Characteristics
- Implicit Memory
- In-group
- In-group Bias
- Inattentional Blindness
- Incarceration
- Incongruence
- Incus
- Independent Variable
- Individual Psychology
- Individual Therapy
- Individualistic Culture
- Inductive Reasoning
- Industrial Organizational Psychology
- Industrial Psychology
- Industrial and Organizational Psychology
- Industrial-organizational (I-O)
- Inferiority Complex
- Inflammatory Pain
- Informational Social Influence
- Informed Consent
- Initiation
- Insomnia
- Instinct
- Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee
- Institutional Review Board
- Instrumental Aggression
- Intake
- Intelligence
- Intelligence Quotient
- Inter-Rater Reliability
- Interaural Level Difference
- Interaural Timing Difference
- Interference
- Internal Factor
- International Classification of Diseases
- Interpersonal
- Interview
- Intrapersonal
- Intrinsic Motivation
- Introduction
- Introspection
- Involuntary Treatment
- Iowa K-12 E-Curriculum
- Iris
- Ivan Pavlov
- James-Lange
- James-Lange Theory of Emotion
- Jean Piaget
- Jet Lag
- Job Analysis
- Job Application
- Job Burnout
- Job Satisfaction
- Job Strain
- Job Training
- John Watson
- Julian Rotter
- Jung
- Just Noticeable Difference
- Just-world Hypothesis
- K-complex
- Karen Horney
- Kinesthesia
- Kinsey
- Kitty Genovese
- Kurt Koffka
- LGBT
- Language
- Latency Period
- Latent Content
- Latent Learning
- Law of Effect
- Lawrence Kohlberg
- Learned Helplessness
- Learning
- Lens
- Leptin
- Lexicon
- Lifespan Development
- Light Wave
- Lillian Gilbreth
- Limbic System
- Linear Perspective
- Locus Coeruleus
- Locus of Control
- Long-term Memory
- Longitudinal Fissure
- Longitudinal Research
- Ltm
- Lucid Dream
- Lymphocyte
- MBTI
- MMPI
- MOBIUS Psychology
- MRI
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging
- Major Depressive Disorder
- Malleus
- Mania
- Manic Episode
- Manifest Content
- Marijuana
- Martin Seligman
- Maslow
- Masters and Johnson
- Max Wertheimer
- Medical Marijuana
- Meditation
- Medulla
- Meissner's Corpuscle
- Melatonin
- Membrane Potential
- Memory
- Memory Consolidation
- Memory Errors
- Memory Sins
- Memory-enhancing Strategy
- Mental Disorders
- Mental Health
- Mental Set
- Mentoring
- Merkel’s Disk
- Meta-analysis
- Metabolic Rate
- Methadone
- Methadone Clinic
- Methamphetamine
- Midbrain
- Minnesota Multiphasic Personality Inventory
- Misattribution
- Misinformation Effect Paradigm
- Mitosis
- Mnemonic
- Mnemonic Device
- Modality
- Model
- Modern Psychology
- Molaison
- Monaural Cue
- Mood Disorder
- Morbid Obesity
- Morpheme
- Motivation
- Motor Cortex
- Motor Skills
- Multicultural Psychology
- Multiple Intelligences Theory
- Mutation
- Myelin Sheath
- Myers-Briggs Type Indicator
- Ménière's Disease
- Müller-Lyer
- NH Psy
- NREM
- Narcissistic Personality Disorder
- Narcolepsy
- Natural Concept
- Natural Selection
- Naturalistic Observation
- Nature
- Nature vs. Nurture
- Negative Affectivity
- Negative Correlation
- Negative Punishment
- Negative Reinforcement
- Negative Symptom
- Neo-Freudians
- Nervous System
- Neurodevelopmental Disorder
- Neuron
- Neuropathic Pain
- Neuroplasticity
- Neuroscience
- Neurosis
- Neurotransmitter
- Neutral Stimulus
- Newborn Reflexes
- Night Terror
- Noam Chomsky
- Nociception
- Nociceptor
- Non-REM
- Nondirective Therapy
- Normative Approach
- Normative Social Influence
- Norming
- Nurture
- O*NET
- OCD
- OCD Circuit
- Obedience
- Obese
- Object Permanence
- Observational Learning
- Observer Bias
- Obsession
- Obsessive-compulsive Disorder
- Obsessive-compulsive Personality Disorder
- Obsessive-compulsive and Related Disorders
- Obstructive Sleep Apnea
- Occipital Lobe
- Occupational Stress
- Olfactory Bulb
- Olfactory Receptor
- Open Washington
- OpenWA
- Openstax
- Operant Conditioning
- Operational Definition
- Opiate
- Opinion
- Opioid
- Opponent-process Theory of Color Perception
- Optic Chiasm
- Optic Nerve
- Optimism
- Oral Stage
- Organizational Culture
- Organizational Psychology
- Orgasm
- Out-group
- Overgeneralization
- Overweight
- PET Scan
- PSYC 203 Intro to Psychology
- PTSD
- Pacinian Corpuscle
- Pain
- Pancreas
- Panic Attack
- Panic Disorder
- Paranoid Delusion
- Paranoid Personality Disorder
- Parasomnia
- Parietal Lobe
- Partial Reinforcement
- Participant
- Pattern Perception
- Pavlov
- Peak
- Peer-reviewed Journal Article
- Perceived Control
- Perception
- Perceptual Hypotheses
- Performance Appraisal
- Performance Review
- Peripartum-onset Depression
- Peripheral Nervous System
- Peripheral Route Persuasion
- Permissive Parenting Style
- Persistence
- Persistent Depressive Disorder
- Personality
- Personality Assessment
- Personality Disorder
- Personality Psychology
- Personality Test
- Personality Trait
- Personality Type
- Personality testing
- Persuasion
- PhD
- Phallic Stage
- Phenotype
- Pheromone
- Philip Zimbardo
- Phineas Gage
- Phobia
- Phoneme
- Photoreceptor
- Physical Dependence
- Physical Development
- Pineal Gland
- Pinna
- Pitch
- Pituitary Gland
- Place Theory of Pitch Perception
- Placenta
- Plateau
- Play Therapy
- Polygenic
- Polygraph
- Pons
- Population
- Positive Affect
- Positive Correlation
- Positive Psychology
- Positive Punishment
- Positive Reinforcement
- Positron Emission Tomography
- Postdoctoral Training Program
- Postpartum Depression
- Posttraumatic Stress Disorder
- Practical Intelligence
- Prader-Willi Syndrome
- Prefrontal Cortex
- Prejudice
- Prenatal Care
- Prenatal Development
- Preoperational
- Primary Appraisal
- Primary Reinforcer
- Primary Sexual Characteristics
- Principle of Closure
- Proactive Interference
- Problem-focused Coping
- Problem-solving Strategy
- Procedural Justice
- Procedural Memory
- Prodromal Symptom
- Product Placement
- Projection
- Projective Test
- Proprioception
- Prosocial
- Prosocial Behavior
- Prototype
- Proximity
- PsyD
- Psyche
- Psychoanalysis
- Psychoanalyst
- Psychoanalytic Theory
- Psychobiology
- Psychodynamic Therapy
- Psychological Dependence
- Psychological Disorder
- Psychological Disorders
- Psychological Research
- Psychologists
- Psychology
- Psychology Careers
- Psychology Employment
- Psychoneuroimmunology
- Psychopathology
- Psychophysiological Disorders
- Psychosexual Development
- Psychosexual Stages of Development
- Psychosocial Development
- Psychotherapy
- Psychotropic
- Punishment
- Pupil
- RBD
- REM
- REM Sleep Behavior Disorder
- RISB
- Racism
- Random Assignment
- Random Sample
- Range of Reaction
- Rapid Eye Movement
- Rational Emotive Therapy (RET)
- Rationalization
- Reaction Formation
- Real Self
- Recall
- Receptor
- Recessive Allele
- Reciprocal Determinism
- Reciprocity
- Recognition
- Reconstruction
- Reflex
- Refractory Period
- Regression
- Reinforcement
- Relapse
- Relationships
- Relaxation Response Technique
- Relearning
- Reliability
- Replication
- Representative Bias
- Representative Sample
- Repression
- Research Ethics
- Research Methods
- Research Regulation
- Resistant Attachment
- Resolution
- Response-based Stress
- Resting Potential
- Restless Leg Syndrome
- Reticular Formation
- Retina
- Retrieval
- Retroactive Interference
- Retrograde Amnesia
- Reuptake
- Reversibility
- Richard Rahe
- Rods
- Rogerian Therapy
- Role Schema
- Romantic Love
- Rorschach Inkblot Test
- Rotating Shift Work
- Rotter Incomplete Sentence Blank
- Ruffini Corpuscle
- Rumination
- SCN
- SIDS
- SRRS
- STM
- Safety Behavior
- Sample
- Satiation
- Scapegoating
- Schachter-Singer
- Schachter-Singer Two-factor Theory of Emotion
- Schema
- Schemata
- Schiavo
- Schizoid Personality Disorder
- Schizophrenia
- Schizotypal Personality Disorder
- Scientific Management
- Scientific Method
- Scientific Research
- Script
- Seasonal Pattern Depression
- Second-order Conditioning
- Secondary Appraisal
- Secondary Reinforcer
- Secure Attachment
- Secure Base
- Selective Migration
- Self Concept
- Self-Efficacy
- Self-disclosure
- Self-efficacy Abilities
- Self-fulfilling Prophecy
- Self-reference Effect
- Self-serving Bias
- Semantic Encoding
- Semantic Memory
- Semantics
- Semipermeable Membrane
- Sensation
- Sensation and Perception
- Senses
- Sensorimotor
- Sensorineural Hearing Loss
- Sensory Adaptation
- Sensory Memory
- Set Point Theory
- Sex Characteristics
- Sex Drive
- Sexism
- Sexual Harassment
- Sexual Orientation
- Sexual Response Cycle
- Shaping
- Short-term Memory
- Sickle Cell Anemia
- Sigmund Freud
- Signal Detection Theory
- Similarity
- Single-blind Study
- Situational
- Skinner
- Skinner Box
- Sleep
- Sleep Apnea
- Sleep Debt
- Sleep Deprivation
- Sleep Disorders
- Sleep Problems
- Sleep Rebound
- Sleep Regulation
- Sleep Spindle
- Sleep Stages
- Sleepwalking
- Social Anxiety Disorder
- Social Exchange Theory
- Social Facilitation
- Social Loafing
- Social Norm
- Social Psychology
- Social Readjustment Rating Scale
- Social Role
- Social Support
- Social-cognitive Theory
- Social/Behavioral Sciences
- Society for Industrial and Organizational
- Sociocultural Treatment
- Socioemotional Selectivity Theory
- Sodium-potassium Pump
- Solomon Asch
- Soma
- Somatic Delusion
- Somatic Nervous System
- Somatosensory Cortex
- Somatosensory System
- Somatotype
- Somnambulism
- Sound
- Sound Wave
- Specific Phobia
- Spermarche
- Spinal Cord
- Spontaneous Recovery
- Sport and Exercise Psychology
- Stage 1 Sleep
- Stage 2 Sleep
- Stage 3 Sleep
- Stage 4 Sleep
- Stage of Exhaustion
- Stage of Resistance
- Stages of Moral Reasoning
- Standard Deviation
- Standardization
- Stanford Prison Experiment
- Stanley Milgram
- States of Consciousness
- Statistical Analysis
- Stereoblindness
- Stereotype
- Stimulant
- Stimulus Discrimination
- Stimulus Generalization
- Stimulus-based Stress
- Storage
- Strategic Family Therapy
- Stress
- Stress Management
- Stress Reduction
- Stressors
- Stroop Effect
- Structural Family Therapy
- Structuralism
- Studying
- Sublimation
- Subliminal Message
- Substance Abuse
- Substantia Nigra
- Sudden Infant Death Syndrome
- Suggestibility
- Suicidal Ideation
- Suicide
- Sulci
- Superego
- Supernatural
- Suprachiasmatic Nucleus
- Survey
- Sybil Eysenck
- Sympathetic Nervous System
- Synapse
- Synaptic Vesicle
- Syntax
- Systematic Desensitization
- TAT
- TEMAS
- TEMAS Multicultural Thematic Apperception Test
- Taste
- Taste Aversion
- Taste Bud
- Telecommuting
- Telomere
- Temperament
- Temporal Lobe
- Temporal Theory of Pitch Perception
- Tension Headache
- Teratogen
- Terminal Button
- Test bank
- Thalamus
- Thematic Apperception Test
- Theory
- Theory X
- Theory Y
- Therapy
- Thermoception
- Theta Wave
- Thinking
- Thomas Holmes
- Thorndike
- Threshold of Excitation
- Thyroid Gland
- Timbre
- Token Economy
- Tolerance
- Tolman
- Top-down Processing
- Touch
- Trait
- Transactional Leadership Style
- Transduction
- Transference
- Transformational Leadership Style
- Transgender Hormone Therapy
- Transience
- Trauma
- Treatment
- Trial and Error
- Triangular Theory of Love
- Triarchic Theory of Intelligence
- Trichromatic Theory of Color Perception
- Trough
- Tuskegee Syphilis Study
- Tympanic Membrane
- Type a
- Type b
- U.S. Equal Employment Opportunity
- Umami
- Unconditional Positive Regard
- Unconditioned Response
- Unconditioned Stimulus
- Unconscious
- Uninvolved Parenting Style
- Vaccinations
- Validity
- Variable
- Variable Interval Schedule
- Variable Ratio Schedule
- Ventral Tegmental Area
- Ventricle
- Vertigo
- Vestibular Sense
- Vicarious Punishment
- Vicarious Reinforcement
- Virtual Reality Exposure Therapy
- Visible Spectrum
- Vision
- Visual Encoding
- Voluntary Treatment
- WA 100
- Wakefulness
- Walter Cannon
- Walter Mischel
- Washington 100
- Watson
- Wave
- Wavelength
- Wernicke's Area
- What is Personality
- Wilhelm Wundt
- William James
- Withdrawal
- Wolfgang Köhler
- Work Stress
- Work Team
- Working Backwards
- Workplace Design
- Workplace Violence
- Work–family Balance
- Yale Attitude Change Approach
- Yerkes-Dodson
- Zygote
- and Developmental Research Designs
- and Horney
- assessment
- course onvarious fields of psychology
- ethical professional issues couple family therapy
- hallucination
- river-valley-cc
- types of anger
- zoom
- –ology
- License:
- Creative Commons Attribution
- Language:
- English
Education Standards
Learning Domain: Writing for Literacy in History/Social Studies, Science, and Technical Subjects
Standard: Develop the topic thoroughly by selecting the most significant and relevant facts, extended definitions, concrete details, quotations, or other information and examples appropriate to the audience’s knowledge of the topic.
Learning Domain: Writing for Literacy in History/Social Studies, Science, and Technical Subjects
Standard: Use technology, including the Internet, to produce, publish, and update individual or shared writing products in response to ongoing feedback, including new arguments or information.
Learning Domain: Writing for Literacy in History/Social Studies, Science, and Technical Subjects
Standard: Conduct short as well as more sustained research projects to answer a question (including a self-generated question) or solve a problem; narrow or broaden the inquiry when appropriate; synthesize multiple sources on the subject, demonstrating understanding of the subject under investigation.
Learning Domain: Writing for Literacy in History/Social Studies, Science, and Technical Subjects
Standard: Draw evidence from informational texts to support analysis, reflection, and research.
Maryland College and Career Ready English Language Arts Standards
Grades 11-12Learning Domain: Writing for Literacy in History/Social Studies, Science, and Technical Subjects
Standard: Develop the topic thoroughly by selecting the most significant and relevant facts, extended definitions, concrete details, quotations, or other information and examples appropriate to the audience�۪s knowledge of the topic.
Maryland College and Career Ready English Language Arts Standards
Grades 11-12Learning Domain: Writing for Literacy in History/Social Studies, Science, and Technical Subjects
Standard: Use technology, including the Internet, to produce, publish, and update individual or shared writing products in response to ongoing feedback, including new arguments or information.
Maryland College and Career Ready English Language Arts Standards
Grades 11-12Learning Domain: Writing for Literacy in History/Social Studies, Science, and Technical Subjects
Standard: Conduct short as well as more sustained research projects to answer a question (including a self-generated question) or solve a problem; narrow or broaden the inquiry when appropriate; synthesize multiple sources on the subject, demonstrating understanding of the subject under investigation.
Maryland College and Career Ready English Language Arts Standards
Grades 11-12Learning Domain: Writing for Literacy in History/Social Studies, Science, and Technical Subjects
Standard: Draw evidence from informational texts to support analysis, reflection, and research.
Cluster: Text Types and Purposes.
Standard: Develop the topic thoroughly by selecting the most significant and relevant facts, extended definitions, concrete details, quotations, or other information and examples appropriate to the audience’s knowledge of the topic.
Cluster: Production and Distribution of Writing.
Standard: Use technology, including the Internet, to produce, publish, and update individual or shared writing products in response to ongoing feedback, including new arguments or information.
Cluster: Research to Build and Present Knowledge.
Standard: Conduct short as well as more sustained research projects to answer a question (including a self-generated question) or solve a problem; narrow or broaden the inquiry when appropriate; synthesize multiple sources on the subject, demonstrating understanding of the subject under investigation.
Cluster: Research to Build and Present Knowledge.
Standard: Draw evidence from informational texts to support analysis, reflection, and research.
Psychology
Psychology is designed to meet scope and sequence requirements for the single-semester introduction to psychology course. The book offers a comprehensive treatment of core concepts, grounded in both classic studies and current and emerging research. The text also includes coverage of the DSM-5 in examinations of psychological disorders. Psychology incorporates discussions that reflect the diversity within the discipline, as well as the diversity of cultures and communities across the globe.
Senior Contributing Authors
Rose M. Spielman, Formerly of Quinnipiac University
Contributing Authors
Kathryn Dumper, Bainbridge State College
William Jenkins, Mercer University
Arlene Lacombe, Saint Joseph's University
Marilyn Lovett, Livingstone College
Marion Perlmutter, University of Michigan

Lesson 1
Introduction
Lesson 2
What Is Psychology?
Lesson 3
History of Psychology
Lesson 4
Contemporary Psychology
Lesson 5
Careers in Psychology

Lesson 1
Introduction
Lesson 2
Why Is Research Important?
Lesson 3
Approaches to Research
Lesson 4
Analyzing Findings
Lesson 5
Ethics

Lesson 1
Introduction
Lesson 2
Human Genetics
Lesson 3
Cells of the Nervous System
Lesson 4
Parts of the Nervous System
Lesson 5
The Brain and Spinal Cord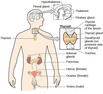
Lesson 6
The Endocrine System

Lesson 1
Introduction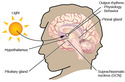
Lesson 2
What Is Consciousness?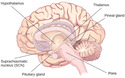
Lesson 3
Sleep and Why We Sleep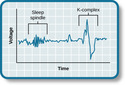
Lesson 4
Stages of Sleep
Lesson 5
Sleep Problems and Disorders
Lesson 6
Substance Use and Abuse
Lesson 7
Other States of Consciousness
Lesson 1
Introduction
Lesson 2
Sensation versus Perception
Lesson 3
Waves and Wavelengths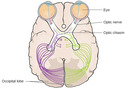
Lesson 4
Vision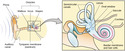
Lesson 5
Hearing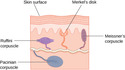
Lesson 6
The Other Senses
Lesson 7
Gestalt Principles of Perception

Lesson 1
Introduction
Lesson 2
What Is Learning?
Lesson 3
Classical Conditioning
Lesson 4
Operant Conditioning

Lesson 1
Introduction
Lesson 2
What Is Cognition?
Lesson 3
Language
Lesson 4
Problem Solving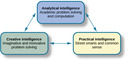

Lesson 6
Measures of Intelligence
Lesson 7
The Source of Intelligence

Lesson 1
Introduction
Lesson 2
How Memory Functions

Lesson 4
Problems with Memory
Lesson 5
Ways to Enhance Memory

Lesson 1
Introduction
Lesson 2
What Is Lifespan Development?
Lesson 3
Lifespan Theories
Lesson 4
Stages of Development
Lesson 5
Death and Dying

Lesson 1
Introduction
Lesson 2
Motivation
Lesson 3
Hunger and Eating
Lesson 4
Sexual Behavior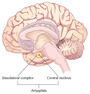
Lesson 5
Emotion

Lesson 1
Introduction
Lesson 2
What Is Personality?

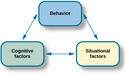
Lesson 5
Learning Approaches
Lesson 6
Humanistic Approaches
Lesson 7
Biological Approaches
Lesson 8
Trait Theorists

Lesson 10
Personality Assessment

Lesson 1
Introduction
Lesson 2
What Is Social Psychology?
Lesson 3
Self-presentation
Lesson 4
Attitudes and Persuasion

Lesson 6
Prejudice and Discrimination
Lesson 7
Aggression
Lesson 8
Prosocial Behavior

Lesson 1
Introduction
Lesson 2
What Is Stress?
Lesson 3
Stressors
Lesson 4
Stress and Illness
Lesson 5
Regulation of Stress
Lesson 6
The Pursuit of Happiness

Lesson 1
Introduction
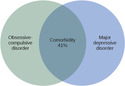


Lesson 5
Anxiety Disorders

Lesson 7
Posttraumatic Stress Disorder
Lesson 8
Mood Disorders
Lesson 9
Schizophrenia
Lesson 10
Dissociative Disorders
Lesson 11
Personality Disorders
Lesson 12
Disorders in Childhood